Contents
The issue of when interest rates go down again is a very popular topic worldwide. Today, we will analyze the possibility of the FED making another cut in 2025. If you recall, the US Federal Reserve had reduced the policy rate by 50 basis points in December 2024 to 4.25-.4.50. It also emphasized that there would be no additional cuts in the near future. First of all, it should be noted that when it comes to high interest rates, it does not matter whether you live in America, a Northern European country or the Middle East.
In this context, according to known economic theories, no one wants to invest or spend in an environment where interest rates are high. This means a slowdown in the economy, high unemployment and ultimately everyone will suffer. In this context, as we all know, unfortunately, global interest rates have increased due to the high inflation phenomenon that emerged after the Covid-19 outbreak. If your financial literacy level is even medium, you know already the subject.
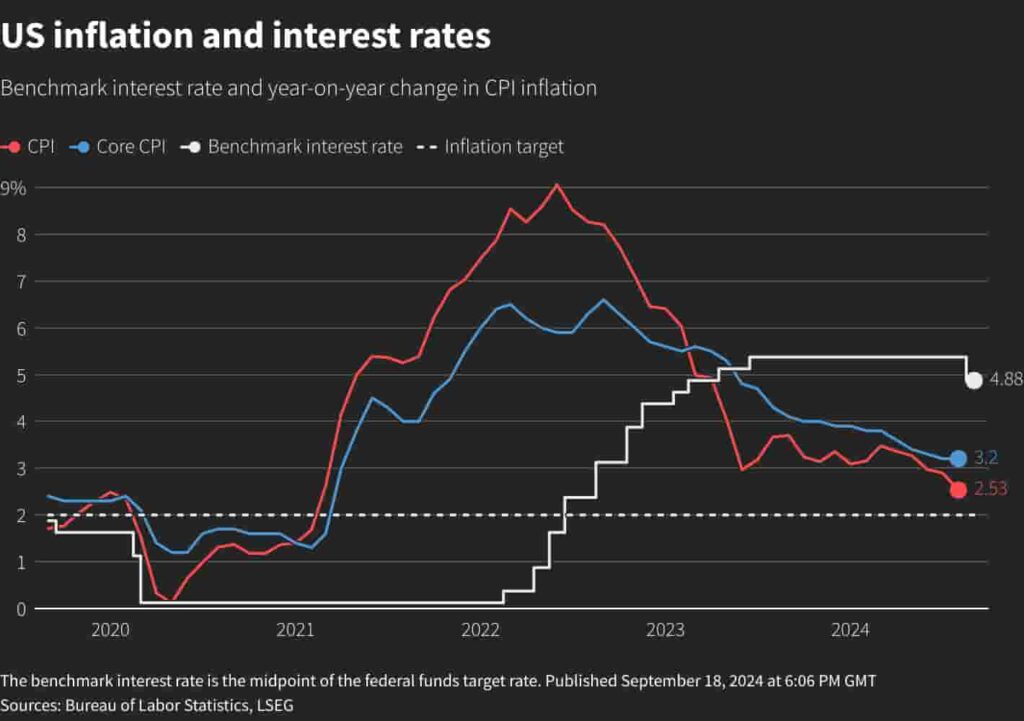
At this point, if you have not read our article explaining the reasons for the interest rate increase, we recommend that you do so first. As you may recall, the disruption of supply chains, the beginning of the Russia-Ukraine war, and the sudden increase in energy and wheat prices caused high inflation globally. In the fight against inflation, central banks almost everywhere in the world, especially the FED and ECB, increased interest rates. In this high interest rate environment, instead of taking risks, trading, or investing, we homo economicus usually prefer to earn risk-free and effortless income by investing our savings or money in interest.
This situation will definitely stop the wheels in the medium and long term and increase unemployment. Well, isn’t economics the science of managing contradictory goals with maximum benefit and profit? Today, as we have just entered 2025, the question on everyone’s mind is when will interest rates fall further globally. Right now, unfortunately, rates are still high.
FED Impact on Global Interest Rate Cuts
Here we will analyse this issue a little. On the other hand, while examining this issue, we will explain it in a way that readers who have not studied economics can understand. That is, we choose to explain it with current examples without overwhelming you with technical terms. First of all, let us state that the most important move in global interest rate cuts is the FED interest rate cut.
If the FED, which constitutes the majority of the world economy, reduces interest rates, other central banks will probably follow the same path.
The main points we will cover here are:
- When will the FED reduce interest rates? How many rate cuts will happen?
- Base Effect on Inflation.
- Is Foreign Exchange Reserve Status Important?
- Will prices fall when inflation decreases?
- What happens if loan interest rates decrease?
Why Do Central Banks Lower Interest Rates?
In order to answer this question correctly, we first need to remember why interest rates were increased, friends.
So, if you remember, when the phenomenon of high inflation emerged on a global scale after the pandemic, most countries increased rates as part of the fight against inflation.
It should also be reminded that; In America, the FED gradually increased rate to the range of 5.25 – 5.50. In the same direction, the European Central Bank and other developed country central banks also implemented parallel action policies. In other words, it is a clear fact that in order for interest rates go down, inflation must first decrease. At this point, it is necessary to mention the base effect.
We would like to briefly explain these technical terms to you. Because, when we understand the base effect, it is easier to understand why inflation is falling globally.
By the way, we would like to point out that the decrease in inflation is not a decrease in prices, but a decrease in the rate of increase of prices.

The Economic Impact of Falling Interest Rates
When we understand these, we will have a clearer understanding of when interest rates go down. We would now like to explain both issues to you with examples.
Namely:
– Decline in inflation: Normally, inflation is a continuous increase in the general level of prices, but in order to understand the issue more easily, let’s consider an economy where there is only one product. Let’s say 1 apple was worth 1 USD last year and its price increased to 2 USD this year. The inflation rate in this country that year was 100%. When the price of the same apple increases to 2.5 USD next year, the inflation rate will be 25% (from 20 USD to 25).
So, in this example, inflation has dropped sharply from 100% to 25% in two years. On the other hand, the price of apples was 1 USD two years ago and is now 2.5 USD. During this period, if your salary or income does not increase by the rate of increase in the price of apples within 2 years, your purchasing power will decrease by that rate.
– Base Effect: In the normal world, inflation calculation is not made that simple. It is calculated end-to-end, month-to-month, for 1 year, based on a product and service basket containing many items.

Real Example from the Markets
In this context, if we start from the apple example, we actually call the base effect the fact that the price of apples increased by 100 percent from last year to this year, and then the price of apples increased by less, that is, 25 percent next year.
In short, we call the base effect when the data or rates calculated by looking at the previous year decrease or increase significantly compared to the previous year. For example, when calculating inflation in October 2024, monthly rates from October 2023 to October 2024 are used.
If monthly inflation was very high in September 2023, inflation will decrease in October 2024 due to the base effect, as this monthly rate will be removed from the new account.
The Economic Impact of Falling Interest Rates
After explaining why interest rate was risen and the related definitions of inflation, it is time to answer the question of when interest rates go down. Those who have been patient and read this far have actually already answered the question. 😊 Yes, for this rates to fall, inflation must first fall. In order to reduce inflation, both monetary and fiscal policies must be implemented simultaneously in a “constriction” manner. Here we need to briefly look at the foreign currency, or in popular parlance for developing countries, the “dollar situation”.
As we all know, the biggest economic indicator in developing country for ordinary citizens is the dollar exchange rate. When interest rate rise, people prefer to keep their savings in domestic money and make deposits instead of buying dollars. In this concept, while thinking about when interest rates go down, we should not forget the dollar exchange rate globally.
Here, CDS, risk premium subject, and the Central Banks’ USD reserves come into play. On the other hand, if USD exchange reserves have increased considerably in a country, it means fear of the dollar skyrocketing with the decrease in the rates has also diminished for that developing country. In this concept the relationship between interest rate and CDS premium is also important topic.
In the light of all this information, it should be noted that the month of decline in interest rate, which is indicated by both the base effect, the decline in inflation and foreign exchange reserves, developing countries will probably be soon at the end of 2025 globally.
At this point, the severity of this decrease is as important as the question of when the interest rates go down. In other words, it is important to proceed on the path of rational policies and make gradual moves in this direction.
How Many Cuts from FED in 2025?
However, first of all, it is necessary to talk about the interest rate cuts in America in order to accelerate the interest rate cuts in the world globally. Most recently, in June, 2024 the FED kept interest rates constant for the seventh consecutive time. FED also stated that inflation indicators were not as good as he expected in order to start interest cuts. In this regard, in their statement following the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, it was stated that the latest indicators show that economic activity continues to improve.

After the last interest rate cut in December 2024, it seems that the FED is not considering making additional interest rate cuts in 2025..
After the FED rate cut issue, let’s talk about the scale of the decrease in interest rates. In this context, it should be noted that; In the economy and financial markets, gradual moves and balance are as important as rationality. In addition, there is a risk that the dollar exchange rate will jump if interest rate cuts are made quickly and harshly in developing countries with high sensitivity to the dollar. At this point, interest that will be a few points above inflation, that is, providing real returns, will be welcomed both in terms of investment and loans. Do not forget that economic growth is also important.
If interest rates go down and still remain above inflation, people will want to keep their money in the local currency and get a real return on deposit, even if it is small. On the other hand, businesses or merchants will use loans as loan interest rate decrease, they will create new jobs, stimulate the economy and contribute to the decrease in unemployment.
