Contents
This article is written for informational purposes only and does not contain any investment advice or buy-sell-hold recommendation. Here we will only touch on basis of fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
We have previously mentioned the basic information about stocks in our article “The Stock Market Make You Rich?” In this article, we will briefly take a look at the definitions, contents and differences of fundamental and technical analysis which are among the most important criteria in stock buying and selling decisions. In other words, we will try to explain what the content and sub-items of this analysis are or what types of analysis are used when performing technical analysis in a way that even those who are not stock market experts (!) can understand.
Differences Between Technical and Fundamental Analysis
We would like to reiterate that we will not name any stocks at this point and that what is explained is purely for informational purposes. In this context, let us reiterate that as we stated in our article mentioned above, the stock market is a medium or long-term investment tool market and that manipulating the stock market is a crime. Furthermore, it is clear that if stock markers getting rich with sudden movements in the short term is a dream. If we return to our topic, it is clear that; fundamental analysis and technical analysis are the most basic indicators of the value and trading points of the stock market or any asset group.

In other words, some stock market analysts make stock buying and selling decisions based on fundamental analysis indicators while others make their decision based on technical analysis indicators. Meanwhile, we should state that, as in every issue, we should not look at this issue from only one perspective. Both sides have their own advantages and disadvantages. These should be evaluated separately.
What Stocks should I Buy?
In this context, to put it briefly, fundamental analysis gives answer the question of “Which stock should I buy?” while technical analysis seeks to answer the question of “When and at what price should I buy this stock?” At this point, it is clear that both technical and fundamental analysis indicators should be used when making stock decisions. In other words, these two types of analysis are not actually used interchangeably, they are two complementary indicators used together.
Let’s say at the beginning what we would say at the end and emphasize that the two analyses are not in competition with each other. In other words, both analyses have their own pros and cons and one cannot be used instead of the other.

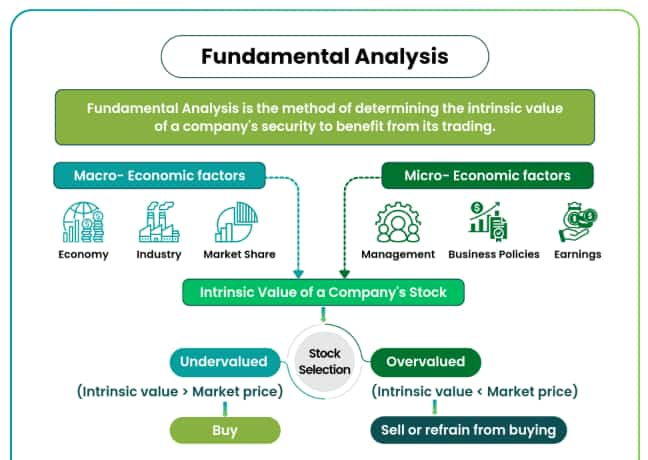
What Is Fundamental Analysis? A Basic Overview
We generally use fundamental analysis when making a decision to buy or sell stocks in the stock market and when looking for an answer to the question of which stock should I invest in. As the name suggests, this type of analysis measures the solidity and financial strength of the company’s foundation. In this context, there are some major ratios and indicators within the scope of fundamental analysis, the names of which we will mention below. On the other hand, not only the company is included in the scope of that analysis. The financial situation of the country, the characteristics of the sector and the international conjuncture will also affect this analysis.
Our main aim here is to determine how much that company is worth and whether there is a difference between its current value and its should value. First, the company’s financial statements are examined and the status of its main indicators is examined.

On the other hand, if we are going to do a fundamental analysis of a company, it would be appropriate to start examining the simplest elements about this company. The first thing to do is to go to the Public Disclosure Platform for the United States by clicking here. (if you live another country, please find its version of your country) Afterwards, you can search and find the relevant company by clicking on the individual or company section on the IAPD website, as seen in the picture below, and selecting the company name or state code.
From the information here, we should question information such as when the company was founded, what the management structure is like or the CVs of the company crucial managers. Such information are important factors in the market value of that company before the financial statements.
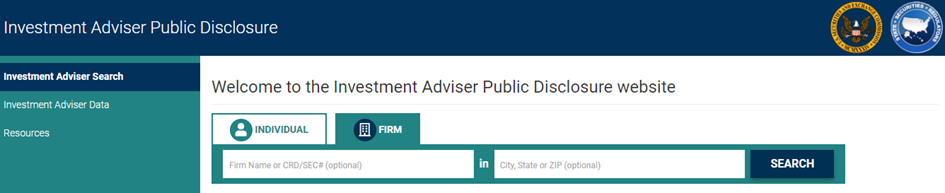
Researching the Firm!
In addition, researching the sector the company is in, the competitive situation in this sector and the position of the company in the sector will also give important ideas. After analysing the company’s IPDP information and sector, we must determine the financial situation of the company by analysing and examining the data we obtain from the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statements we obtain from the financial statements from IPDP.
In this context, some ratios and indicators are used.
Balance Sheet Ratios
As every person who has taken a general accounting course will know, the balance sheet consists of two parts: assets and liabilities. At this point, we would like to point out that the active indicates the company’s assets, that is, the values it owns, and the passive indicates the company’s liabilities, that is, its debts and additionally its capital.
If we list the most frequently used ratios for fundamental analysis in the company’s balance sheet;
– Current Ratio: Tests the business’s ability to pay its short-term debts with current assets. A ratio of 2 or above is considered good.
– Liquidity Ratio: It is the ratio calculated by deducting the stocks from the current ratio. It is expected to be 1 or above.
– Cash Ratio: It is the ratio found by deducting the buyers’ item from the liquidity ratio. A score of 0.20 and above is considered good.
– Debt Ratio: It is the ratio of short and long-term foreign resources to equity capital. A value higher than 1 is not considered good.
– Return on Equity: It is the ratio of equity capital to total net profit. In other words, it is the ratio that shows how much profit a unit of capital brings, and it is very important.
– Inventory Turnover Ratio: It shows how much stocks are sold in a year, and a long period is not considered positive.
– Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: It shows how much receivables are collected in a year. Being short is a positive sign for the firm. It shows that the company has no problems collecting its receivables.

Ratios in Fundamental Analysis
In addition, the following ratios and indicators are also very important in fundamental analysis. We do not give all the formulas and details in order not to get bogged down in technical details 🙂
- Market Value / Book Value
- Price / Earnings (P/E) Ratio
- Horizontal Analysis
- Vertical Analysis
- Leverage Ratio
When we extract these ratios and indicators from the company’s balance sheet and combine them with the data we obtained from IAPD, we reach the results of the fundamental analysis at the same time. As we mentioned before, stocks with solid foundations have potential.
Well, let’s say we decided which stock to buy using fundamental analysis. Now it is time to decide at “what price levels” we should buy or sell these shares.
This is where technical analysis comes into play.

What is Technical Analysis? Pros and Cons of It
Technical analysis can be used to price stocks, commodities, gold prices or the future value of any asset. In this context, we would like to point out that the basic logic of technical analysis is that” every price movement has a pattern.” According to this model, we can predict future price movements using technical analysis from past price movements – other conditions being equal-. However, it should be noted that there should be no expectation that a movement shown by technical analysis will be “definite”.
That is, for example, a sudden political or social event in that country or a development in the sector where the relevant company is located will affect the course of that stock, independent of its own dynamics.
To give an example, let’s say we own a banking stock. When we did the technical analysis of that stock, we predicted that it would go up in the short term and we bought it. However, on that very day, the political authority of that country made a regulation regarding banks that would affect the banks’ profits. In this case, what is expected is that the price of the share we have will go down. However, as a result of the fundamental analysis, the stock’s foundation was solid and according to technical analysis, the upward movement of our stock had begun.
Just like in this example, a stock that is expected to rise or fall according to technical analysis may not go up in stock market terms due to a development independent of the relevant company.
Technical Analysis Ratios
Now let’s talk briefly about the most used terms and indicators in technical analysis:
– Resistance: It represents the upper price at which a stock or security has a lot of sellers and cannot break.
– Support: It represents the lower price at which a security or share has plenty of buyers and does not fall below it.
– Moving Averages: The logic of this indicator is to take the average of past price movements and make predictions for the future.
– RSI (Relative Strength Index): It is a method used to determine whether the relevant stock or security is at overbought or oversold points. If a security’s RSI shows overbought, this is a signal and can be perceived as a warning that sales may come soon.
– Stochastic: This is a different indicator that detects overbought or oversold areas. The measurement method is different compared to RSI.
